Gonorrhea
Q: What is Gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. This spreads by contact with infected bodily fluids through vaginal, oral, or anal sex.
Pregnant women can also pass on the infection to their unborn foetus or to the newborn during childbirth. The infection is easily spread and occurs most often in people who have many sex partners.
Q: How can I get Gonorrhea?
Sexually active men and women can get gonorrhea by having intimate contact or sexual relation with a person who is infected.
Most of the times people infected with gonorrhea do not show symptoms, so to know when to seek medical advice and treatment can be difficult
When symptoms occur, they are often within 2 to 10 days after exposure but may take 30 days too to develop.
Q What are the symptoms of gonorrhea in men and women?
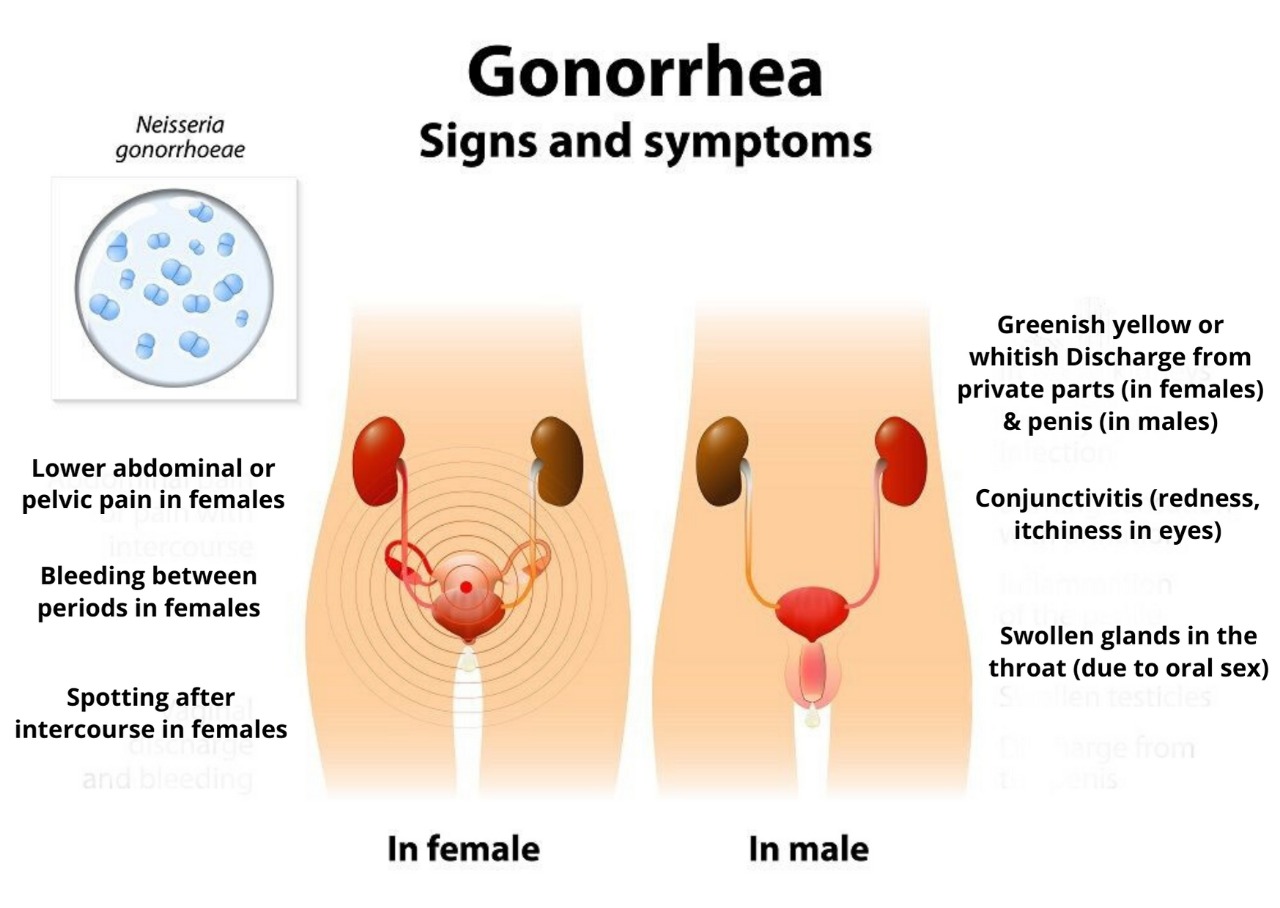
1. Greenish yellow or whitish discharge from the vagina (in females) & penis (in males)
2. Swelling of the vulva (vulvitis) in females & painful and swollen testicles in males
3. Burning while passing urine
4. Conjunctivitis (redness, itchiness in eyes)
5. Lower abdominal or pelvic pain in females
6. Bleeding between periods in females
7. Spotting after intercourse in females
8. Burning in the throat (due to oral sex)
9. Swollen glands in the throat (due to oral sex)
Q How do I know if I have gonorrhea?
If you have sex or intimate contact with a person who has gonorrhea or may have gonorrhea due to relationships with multiple partners, a screening test for gonorrhea is advisable.
You may also look for symptoms of gonorrhea but since most STDs may not show any symptoms for long durations like months to years, taking a test after a potential exposure is recommended by experts.
Q Can I get gonorrhea by kissing or oral
sex?
Yes. Oral sex and deep kissing or french kissing with someone who is infected can lead to gonorrhea of the throat. This is very difficult to distinguish from other common throat infections since the signs and symptoms are very similar.
A throat swab, in case of suspicion, can diagnose Oral Gonorrhea
Q
How do I test for gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea, till some years back, used to be tested by taking a swab sample from the urethra in males as well as females. This method involves the insertion of a swab inside the urinary meatus. Females need a pelvic exam for sample collection. The collected specimen would then be cultured in the lab for identifying the bacteria.
Since this method is invasive and uncomfortable, it is being increasingly replaced by urine-based NAAT or NAT test (Nucleic acid amplification test). The test involves the detection of bacterial DNA using the PCR method in the urine sample.
This is a highly sensitive and specific test and can even detect small amounts of bacterial DNA.
No special preparation is required for this test, except that you may be asked to hold urine for 1 to 2 hours before giving the sample.
Q How is gonorrhea treated?
The treatment of gonorrhea is simple and effective if it is diagnosed early. This involves the use of a combination of oral and injectable antibiotics. Ceftriaxone, a single injection along with oral azithromycin or doxycycline is recommended for the treatment of uncomplicated gonorrhea.
Q
What if I do not take treatment for gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea if left untreated may lead to long term pelvic pain or lower abdominal pain, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and infertility, in women.
In men, the common complications are epididymitis (inflammation of the tubes of the testicles) and rarely infertility.
Gonorrhea, it spreads to the blood stream can affect the heart (endocarditis) or brain (meningitis). These are rare complications of gonorrhea.







